SpaceReeds is a SpaceCoffee team for the CanSat project.
The SpaceReeds CanSat project focuses on developing a miniature satellite designed to measure atmospheric parameters and creating a wireless communication system using a network of relay airborne satellites. The mission aims to explore the use of small communication relays in hard-to-reach or remote regions, such as mountainous areas, where traditional communication infrastructure is limited. The system is designed to support rescue operations and field research by increasing communication capabilities and safety. The name of the team, specifically its member “Reed,” reflects the structure of the network, inspired by the interconnected roots of reeds, symbolizing the interconnected communication nodes of the system.
Mission objectives
The main objective of the mission is to measure temperature, humidity, and air pressure during descent. This data will be used to characterize weather and environmental conditions, providing a basis for a secondary mission.
The secondary mission focuses on creating a wireless communication network using an aerial relay node, represented by CanSat. The goal is to develop a system that enables data exchange between ground stations and remote devices, simulating a satellite network that could be used for communication in mountainous or isolated areas.
During the mission, CanSat will be dropped from a height of approximately 2,500 meters. As it descends, it will record air pressure, temperature, and humidity, while simultaneously transmitting data between two ground computers, creating a simple communication network. The measured parameters will be displayed live at the ground station and stored locally on a microSD card for further analysis.
Mechanical and structural design
CanSat consists of two main parts: the core and the protective casing.
The enclosure, made of translucent 3D-printed PETG, provides both protection and visibility of the internal components. Three metal rods ensure structural integrity and rigidity. The enclosure consists of top and bottom covers, three vertical support beams mounted on the rods, and three side panels that slide into place and are secured with covers.
The inner core contains three vertically mounted mounting plates for sensors, microcontrollers, and other electronic components. This modular design provides easy access to mounting components and batteries while maintaining a compact and durable structure.
Electronics design
The electronics system consists of modules that support both the main and secondary mission objectives. The design focuses on efficient power management, reliable data collection, and stable long-range wireless communication. All components are connected thanks to a compact and modular architecture based on the Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect microcontroller, which manages sensor data, data processing, and communication.
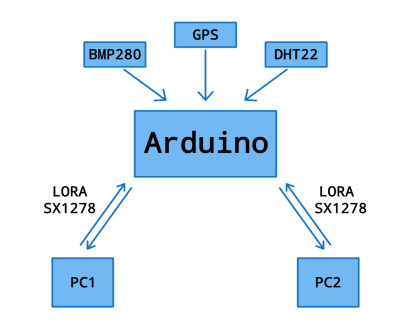
Main mission equipment (recording basic atmospheric parameters):
- BMP280 sensor: measures air pressure (300–1100 hPa) and temperature (from -40°C to +50°C, accuracy ±0.5°C).
- LoRa SX1278 module: transmits measured data from CanSat to the ground station at a frequency of 433 MHz, ensuring stable communication over long distances.
- Waveshare microSD card reader: stores sensor data locally on a microSD card, enabling full data recovery and backup after landing.
These devices form the core of CanSat's environmental monitoring system, providing high-quality data for both scientific analysis and communication testing.
Secondary mission devices (wireless network communication and position tracking):
- LoRa SX1278 module (second unit): Acts as a relay, connecting two or more ground stations via CanSat to establish a communication link.
- GY-NEO6MV2 GPS Module: Determines the geographical location of the CanSat, providing coordinates for live tracking and recovery operations.
- Built-in accelerometer (Arduino): measures acceleration and angular orientation to estimate vertical movement and altitude changes during descent.
- DHT22 sensor: measures air humidity, adding another environmental parameter to improve data quality.
All these components together enable CanSat to serve not only as a probe for collecting data, but also as a functional communication satellite in a miniature ground network.
Power supply
The power subsystem is based on two 18650 lithium-ion cells, each with a capacity of 3350 mAh, providing an estimated operating time of approximately six hours. The configuration provides sufficient current for sensors, data memory, and LoRa modules while maintaining high efficiency. The main challenge in power supply design is to ensure stable voltage for continuous long-range radio communication without excessive power consumption. Energy efficiency is therefore an important factor in both hardware and software implementation.
Communication system
Communication between the mini-satellite and ground infrastructure takes place in the 433 MHz frequency band using LoRaWAN technology, which supports long-distance data exchange with low power consumption. The system enables two-way communication, allowing CanSat to transmit measurement data while simultaneously relaying messages between multiple ground stations. This configuration simulates a network of interconnected nodes, demonstrating the feasibility of using satellite communication relays in remote and inaccessible regions.
Recovery system
The recovery system includes a circular nylon parachute that opens immediately upon release from the rocket, ensuring a controlled descent. A GPS module and antenna help track and locate CanSat during and after its descent, increasing recovery efficiency.
Ground station
During testing, it is planned to deploy multiple ground stations. Each of them will be equipped with an Arduino microcontroller and a LoRa module, creating communication network nodes that will cooperate with the CanSat relay in real time.
Software design
Software written for the project is open source and available in following repositories:
Publicity
The project aims to reach a wide audience through social media. The main channel of communication is TikTok, to which the SpaceReeds team cordially invites all fans of astronomy and memes.
Their TikTok: SpaceReeds
Additional information, including progress reports and articles, is published on Instagram and SpaceCoffee News , promoting the CanSat competition and inspiring young people to explore STEM subjects.
Their Instagram: SpaceReeds